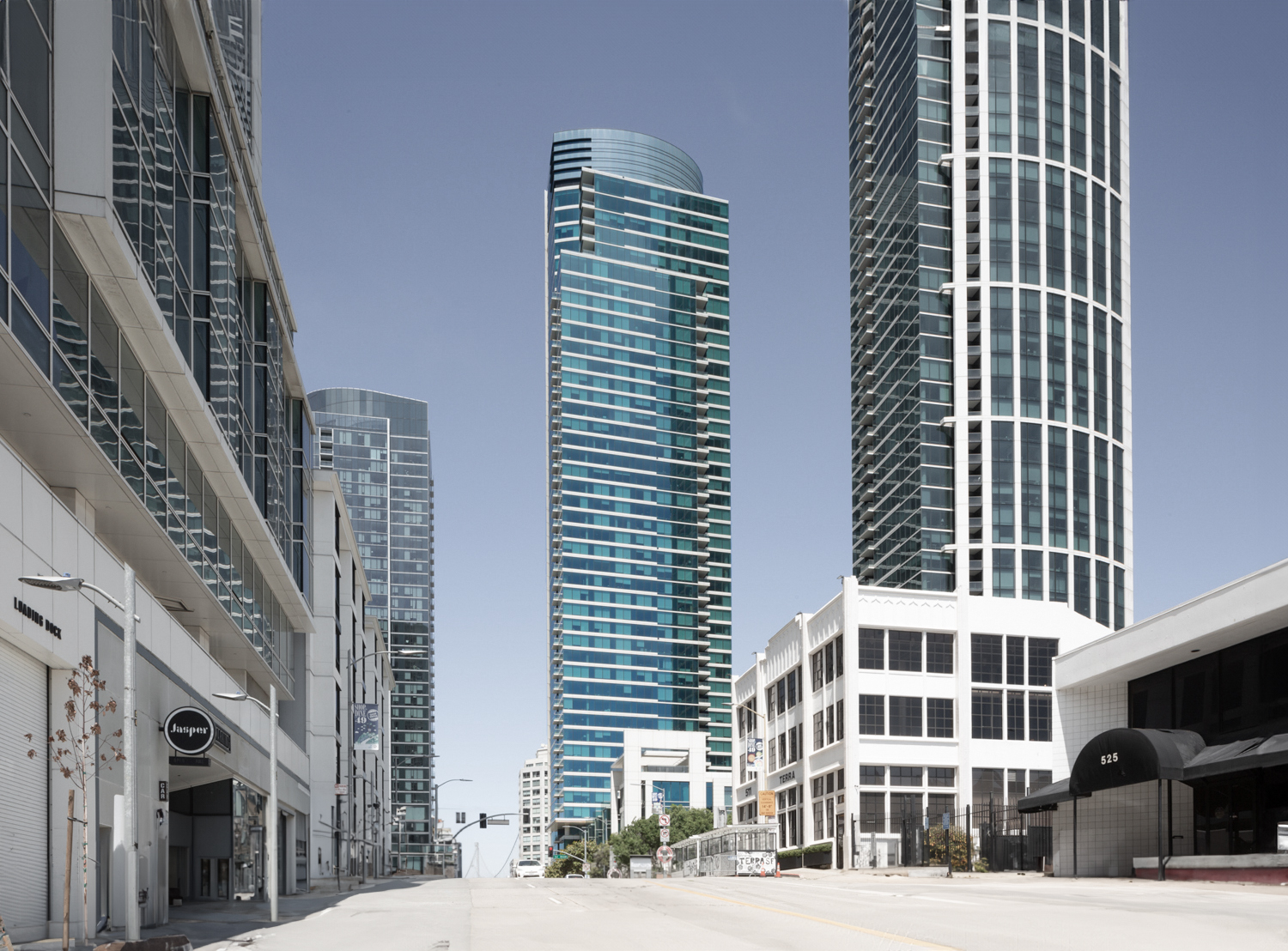
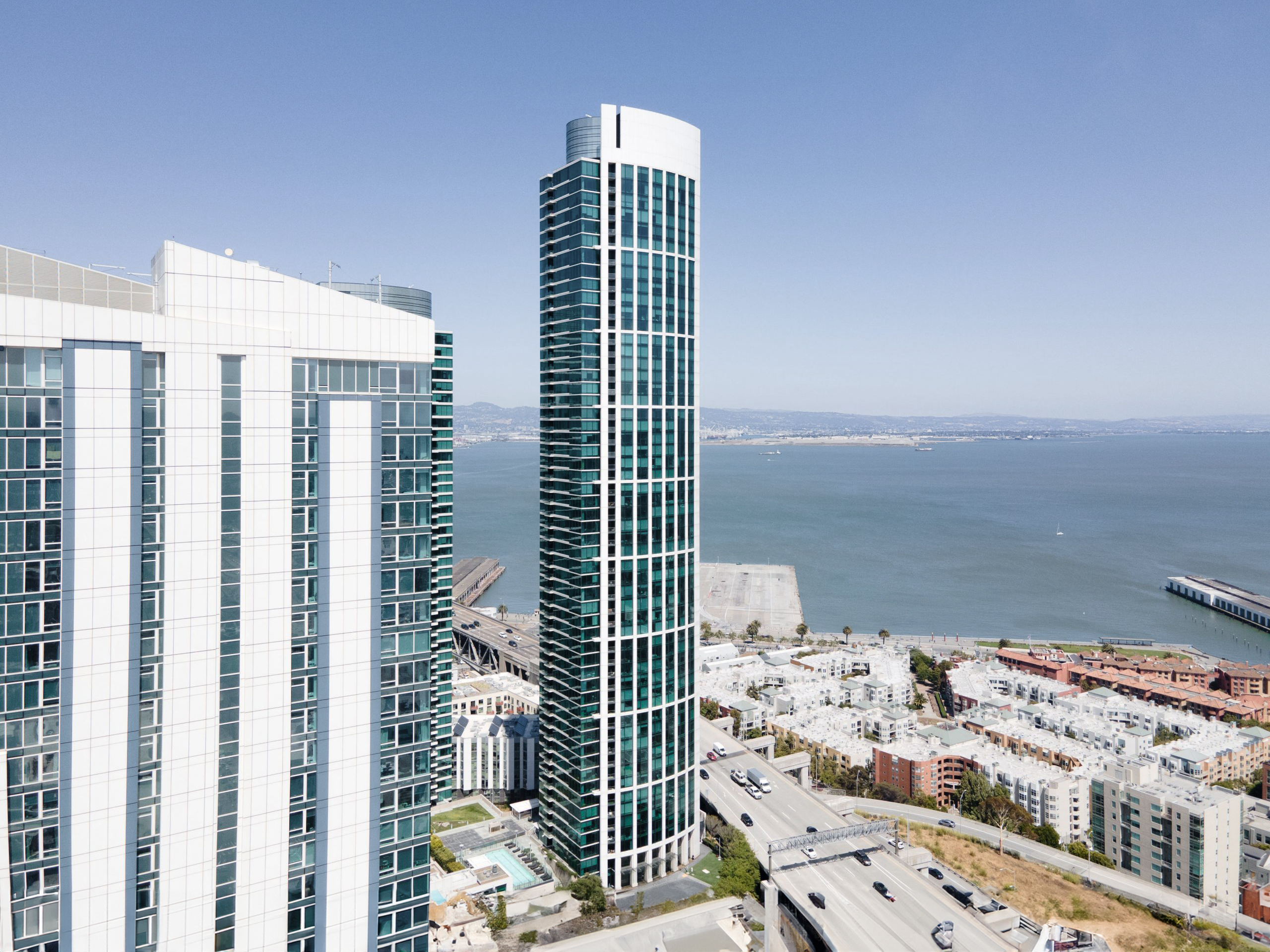
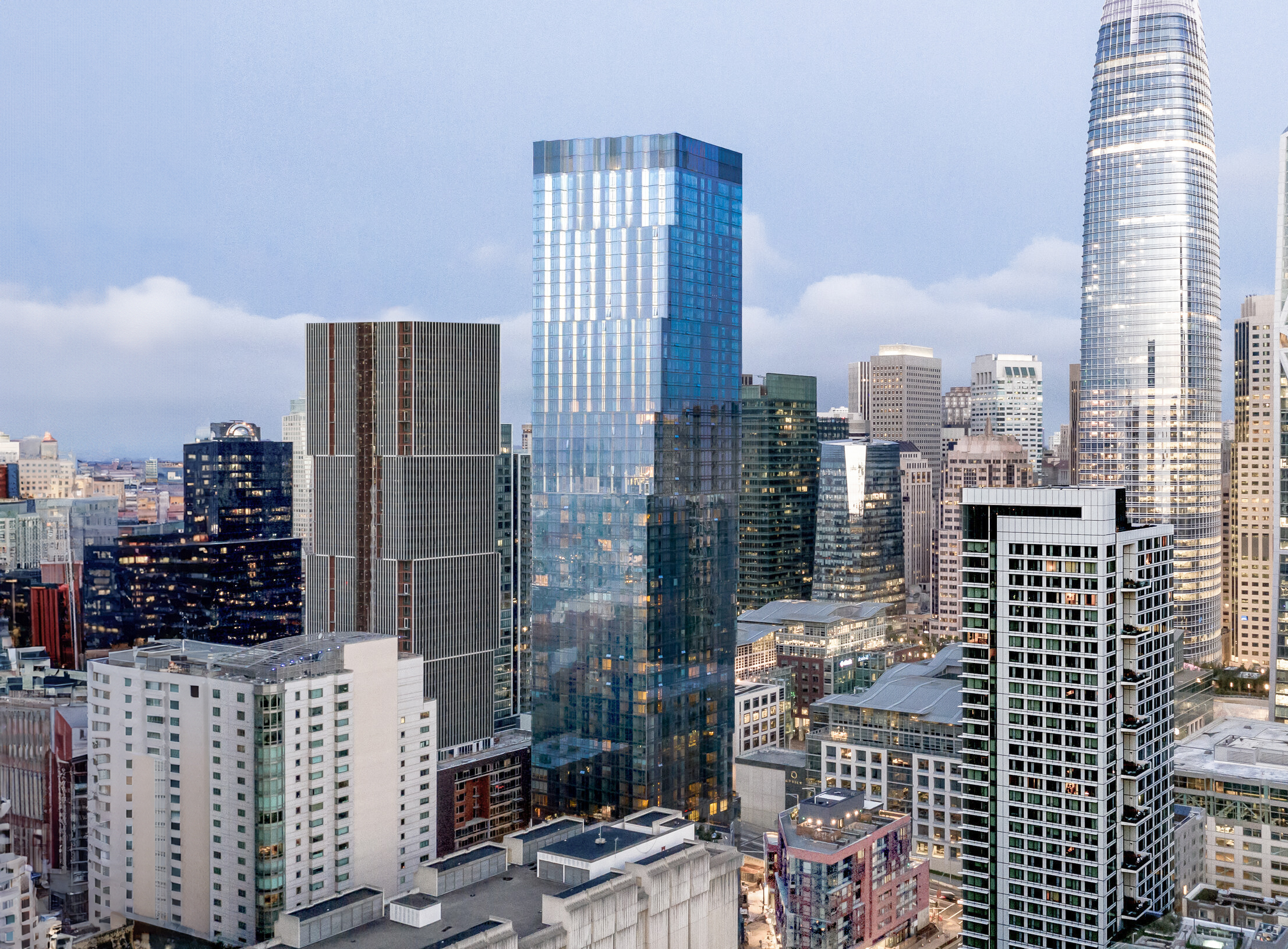
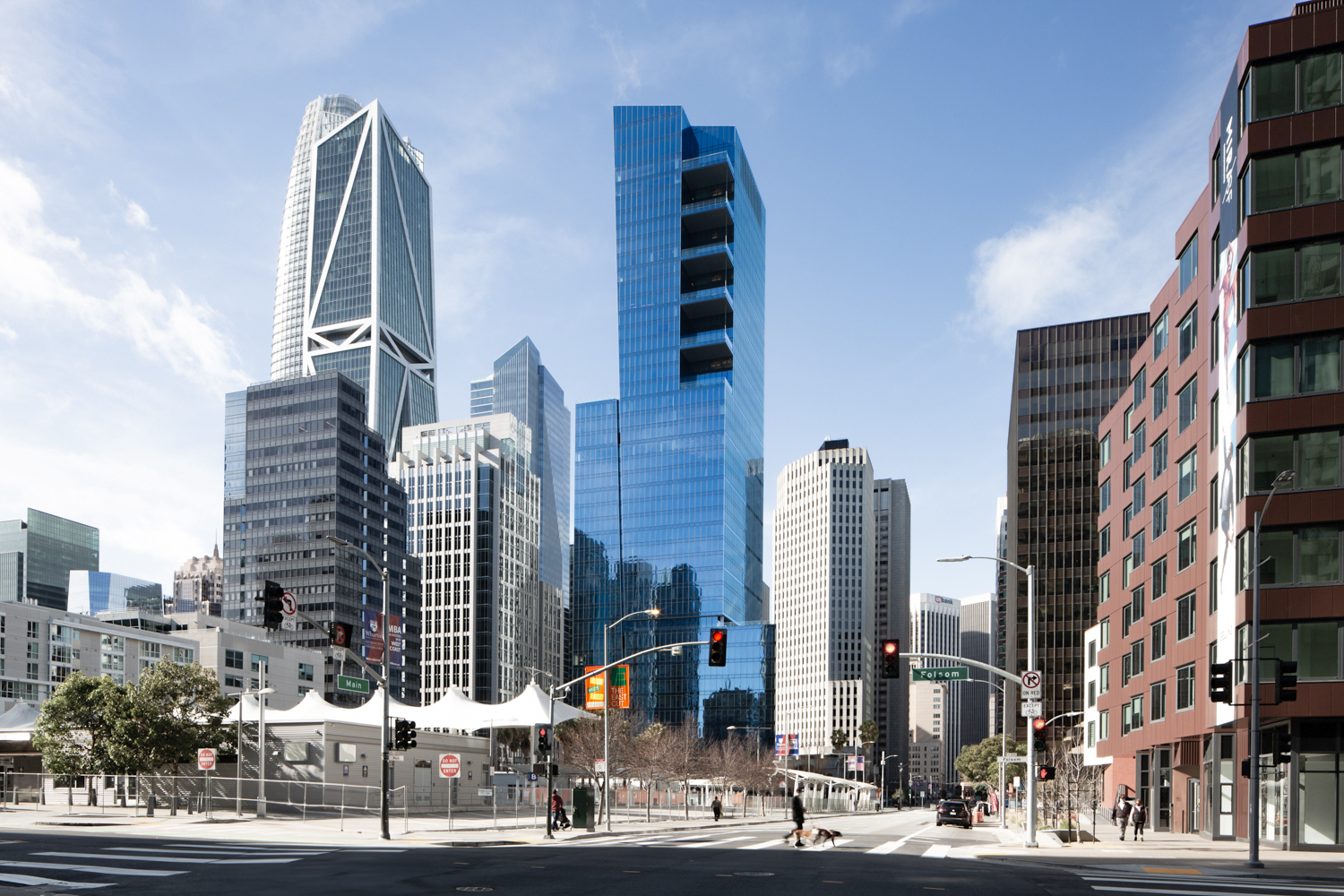
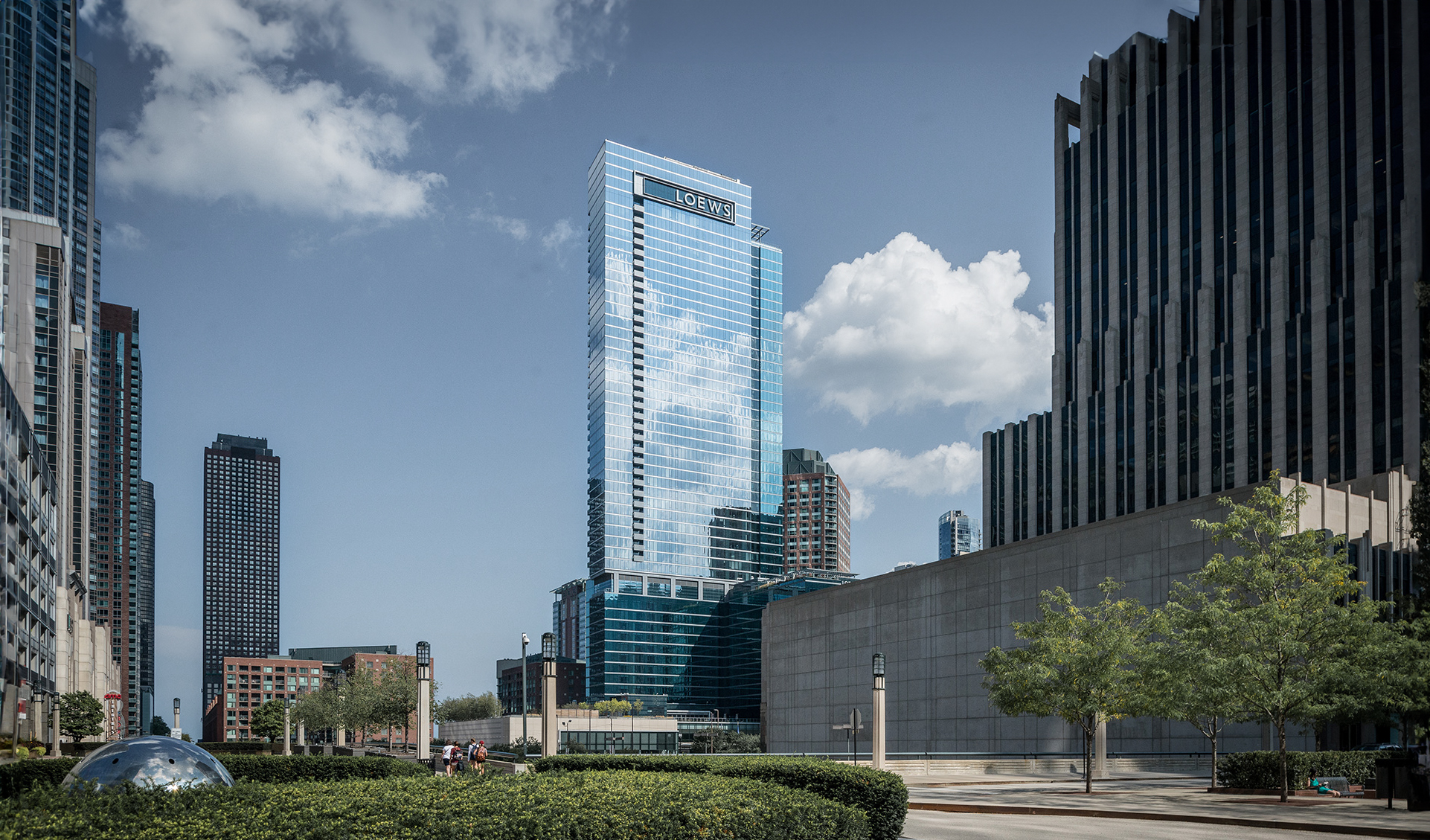
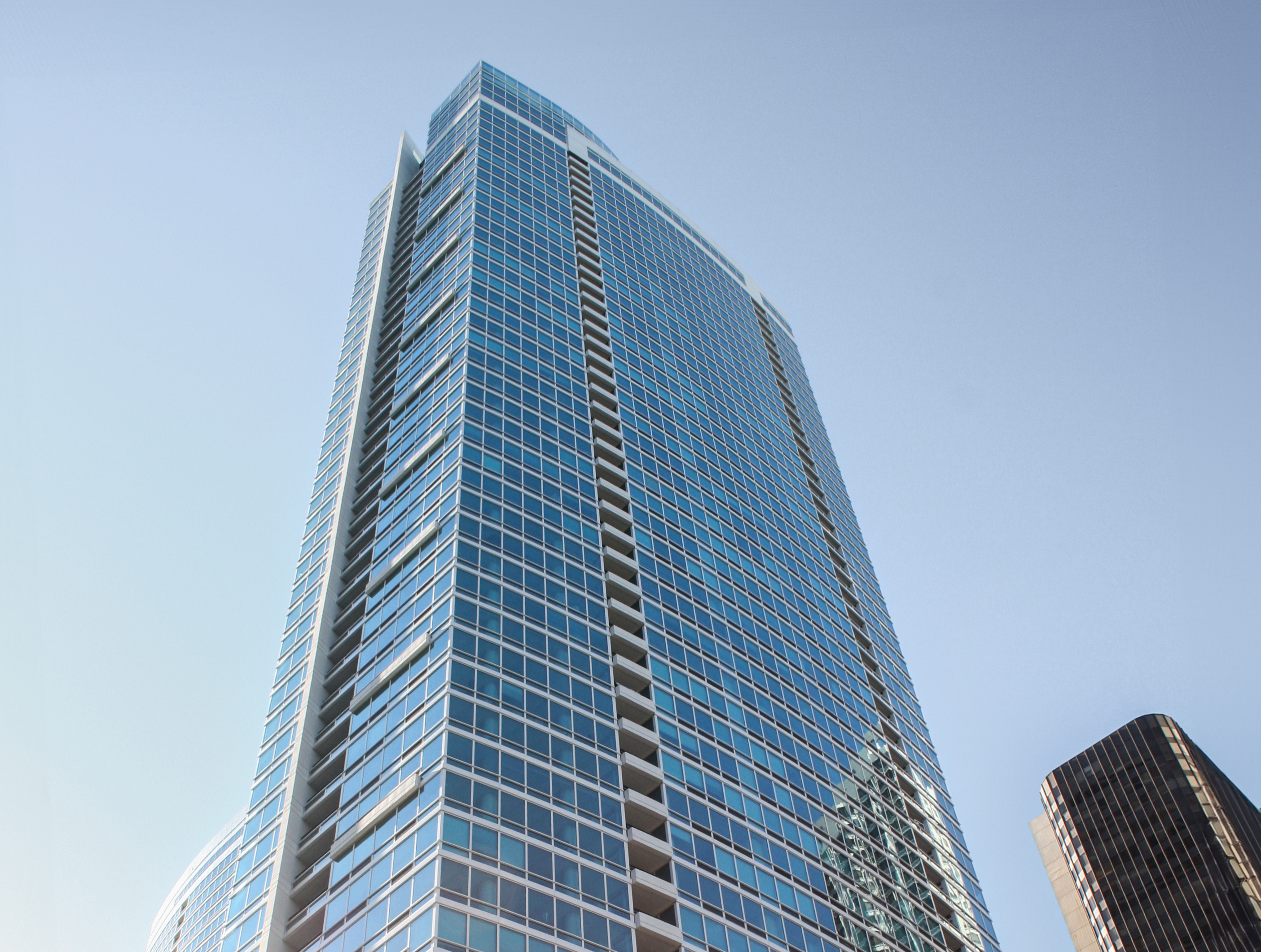
The The Harrison Building is a Contemporary skyscraper designed by Solomon Cordwell Buenz, in association with TSAO Desing Group, and built between 2012 and 2014 in San Francisco, CA.
The Harrison Building is not the only name you might know this building by though. The building is, or has also been known as Tower Two at One Rincon Hill.
Its precise street address is 401 Harrison St, San Francisco, CA. You can also find it on the map here.