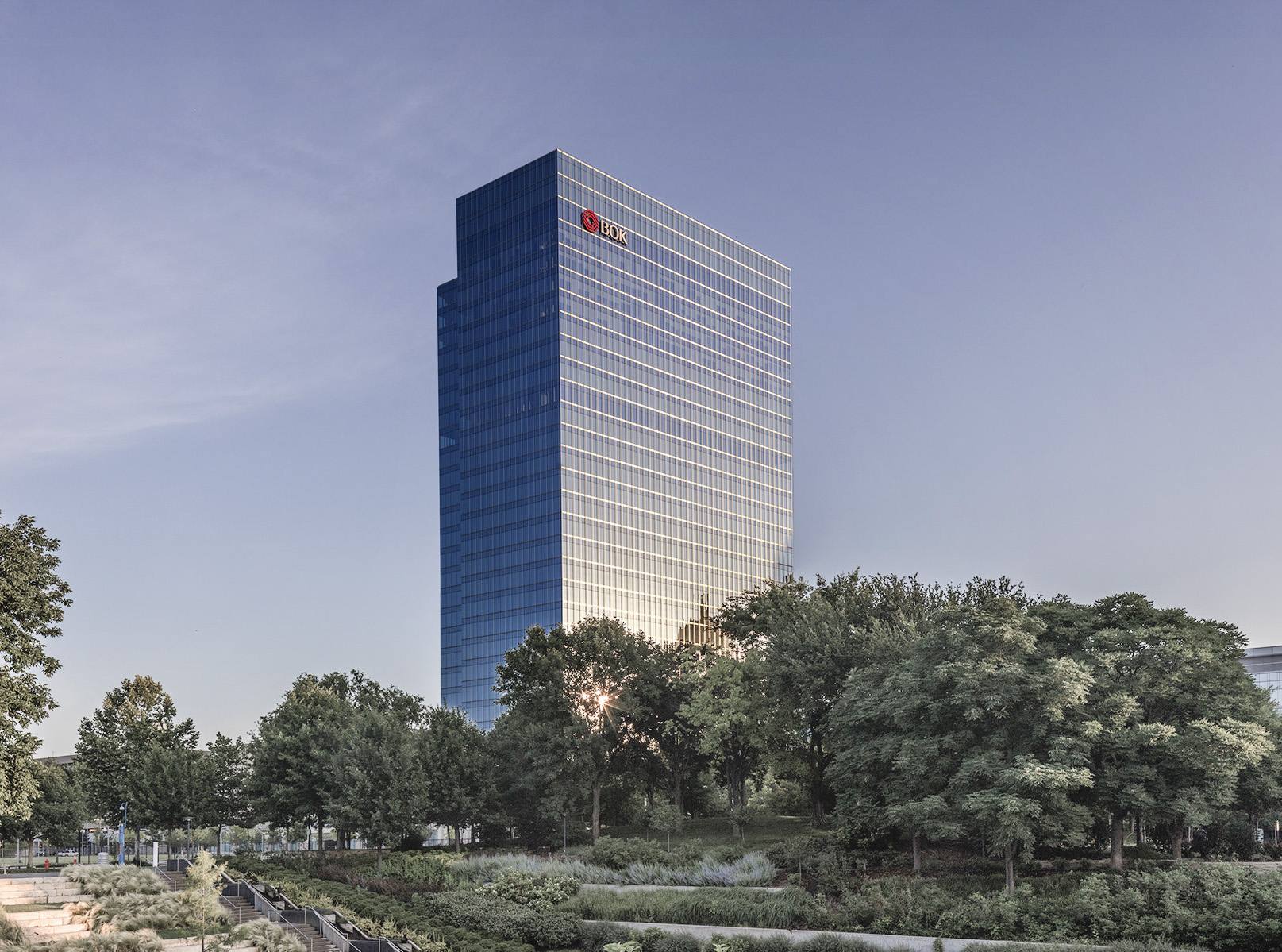
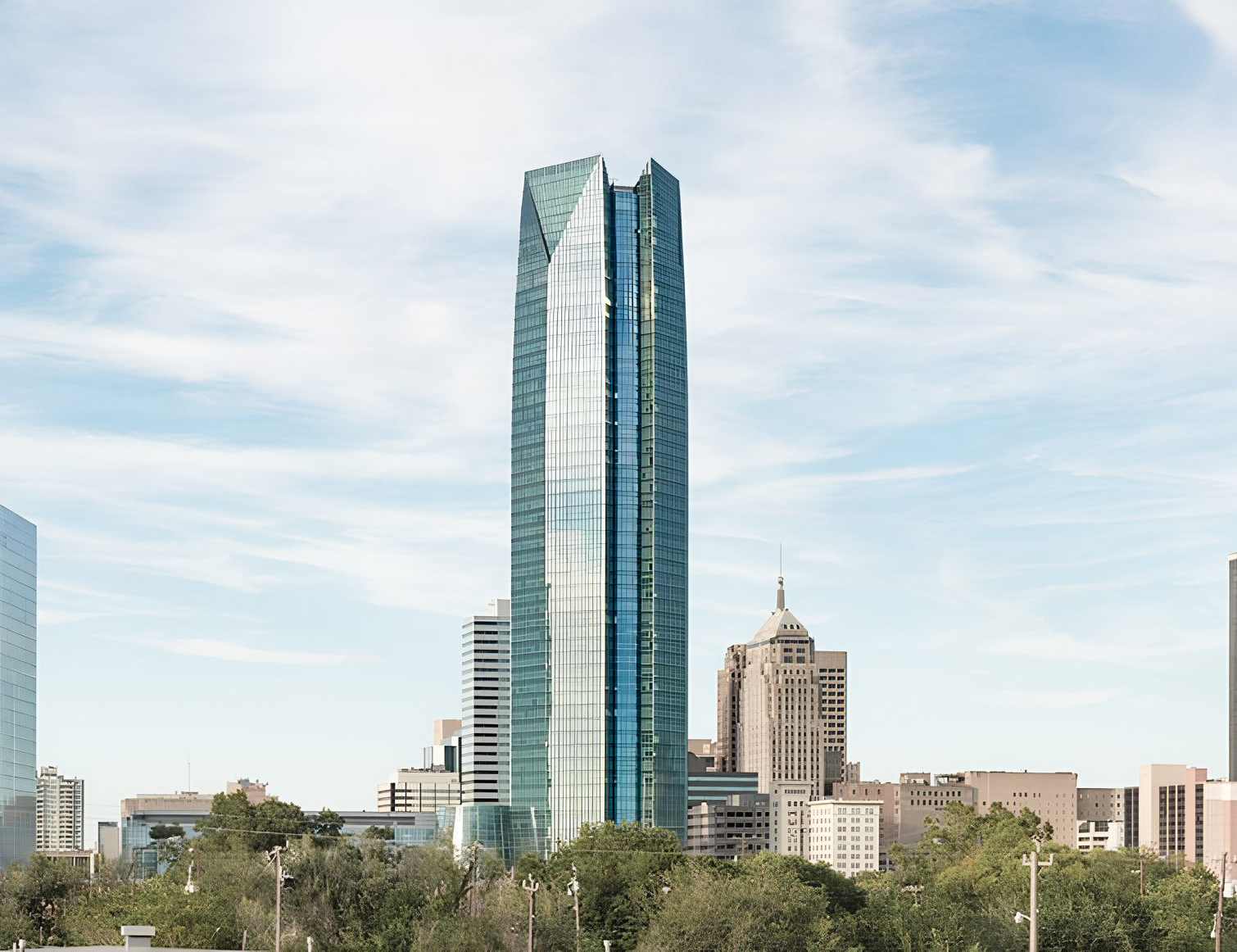
The BOK Park Plaza is a Contemporary skyscraper designed by Pickard Chilton, in association with Kendall/Heaton Associates, and built between 2015 and 2018, for a reported $270 million dollars, in Oklahoma City, OK.
Its precise street address is 499 West Sheridan Avenue, Oklahoma City, OK. You can also find it on the map here.
In 2018 the BOK Park Plaza was awarded with the Mayor's Award for Outstanding Development .
The Union Bus Station, the Auto Hotel, the Black Hotel, and the Carpenter Square Theatre were demolished to make way for the new development.
However, in the annex structures, especially the north garage, Art Deco components and original elements from the former Union Bus Station, including the iconic sign, were incorporated, restored, and protected behind a glass ‘lantern’ on the facade..