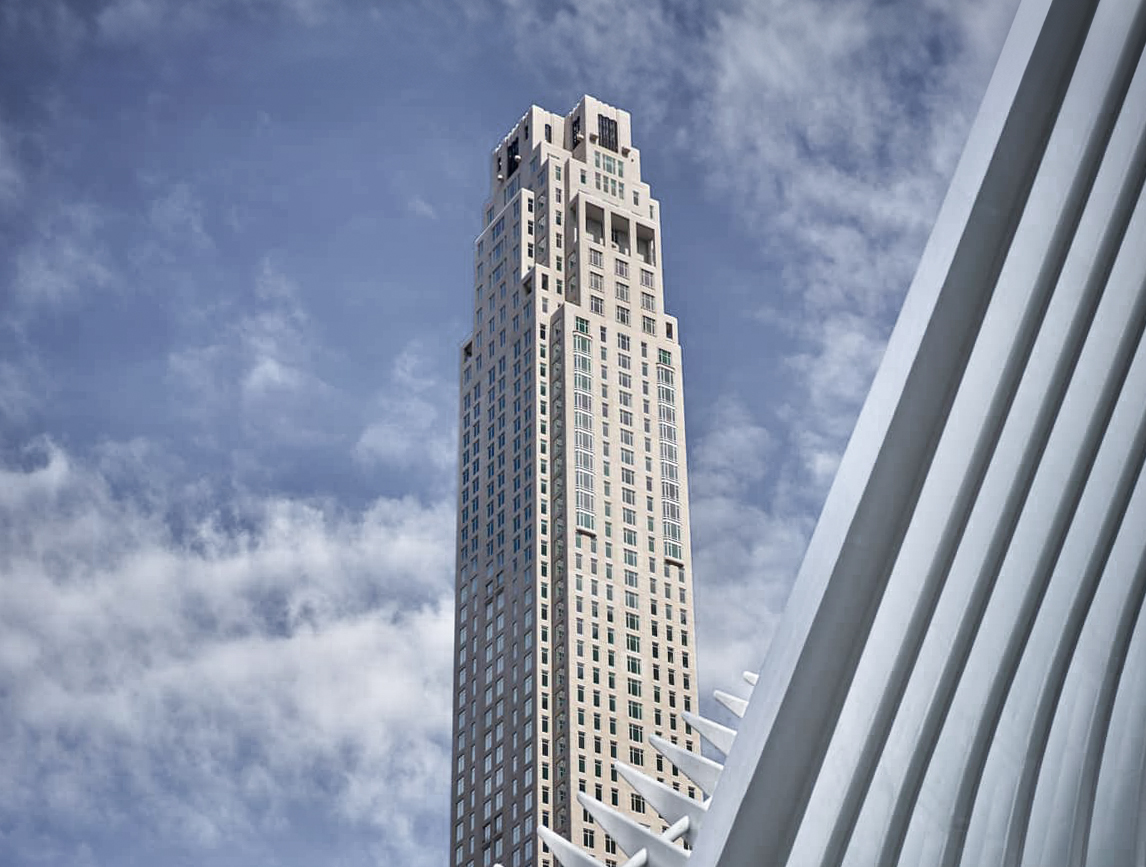
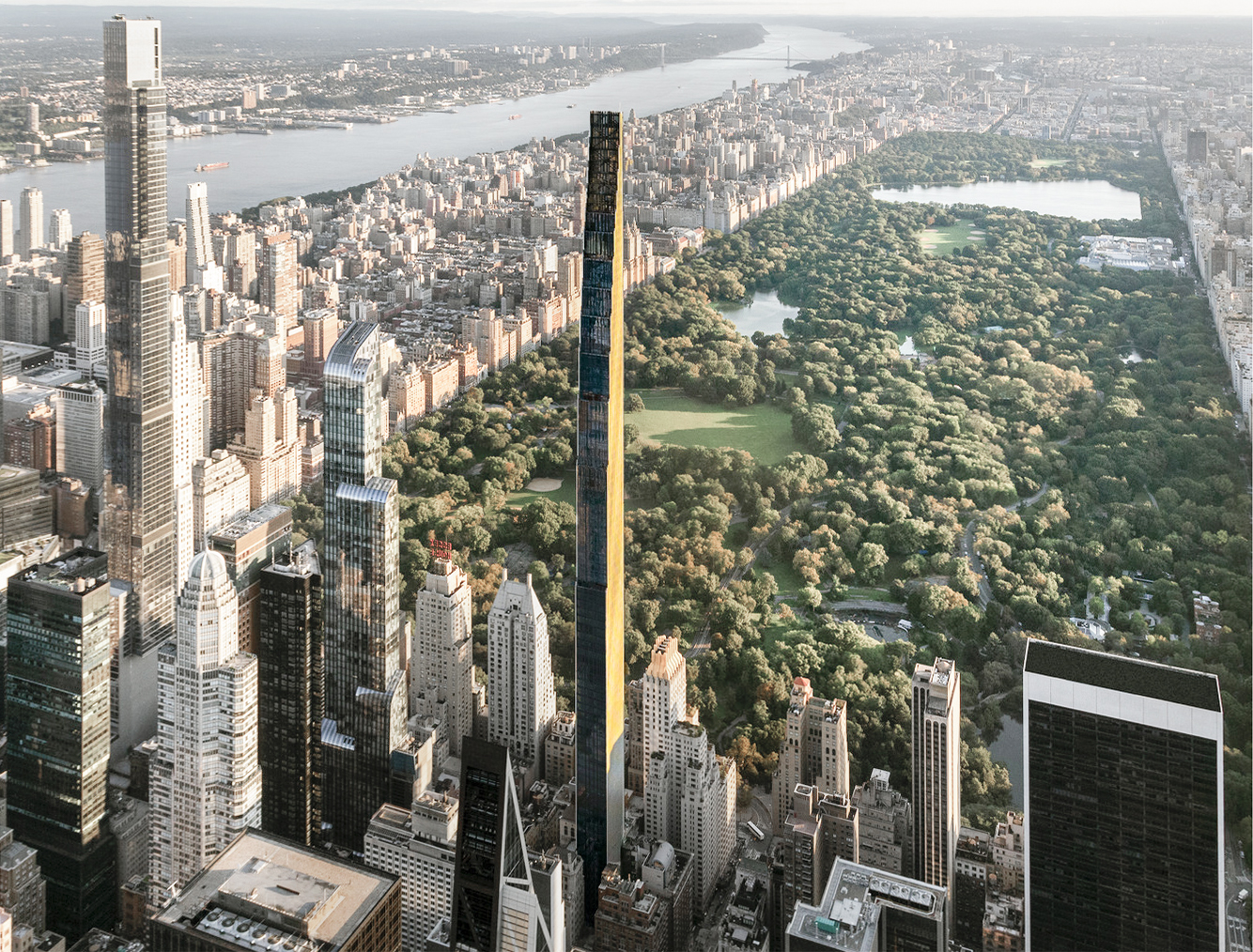
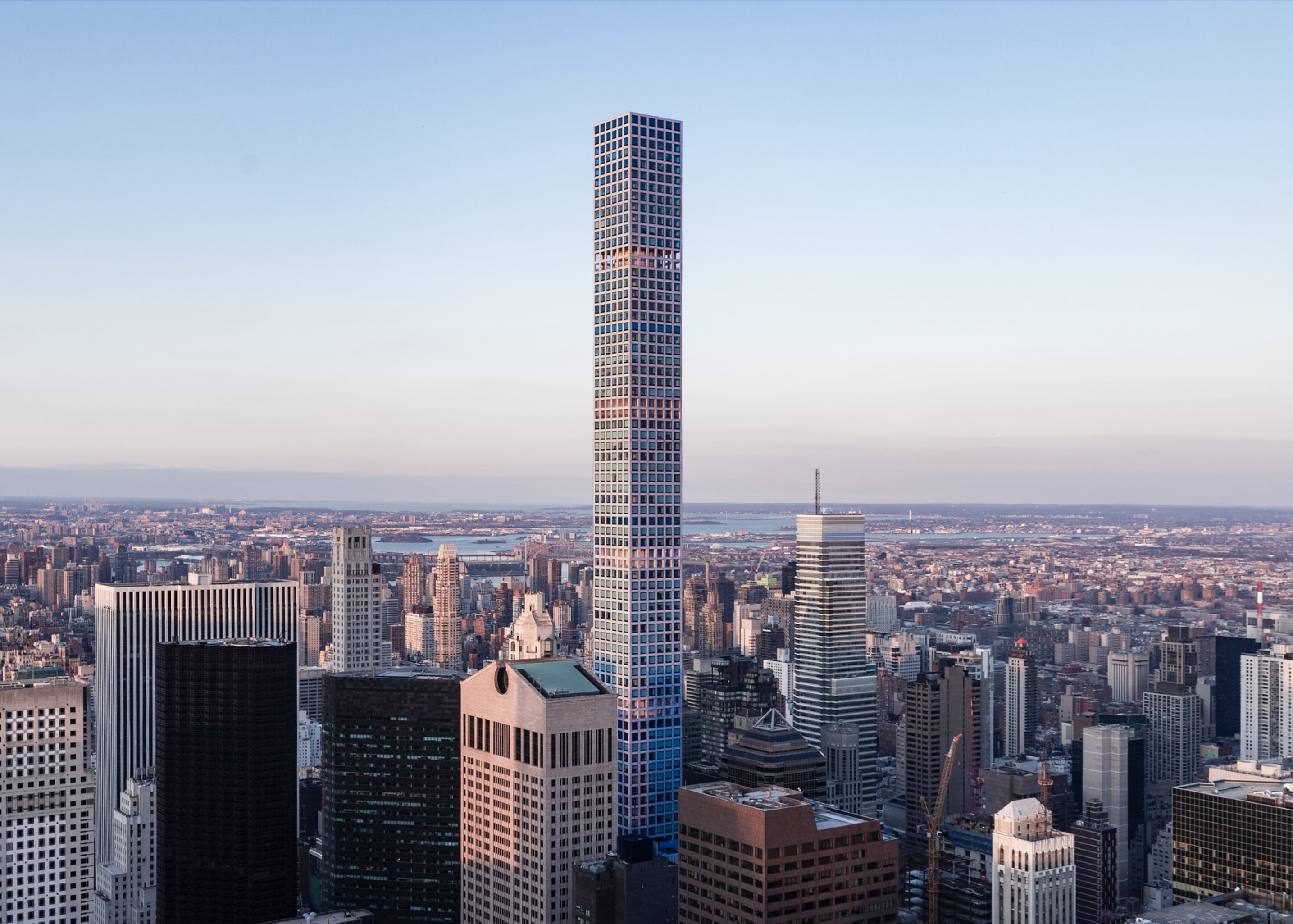
The Central Park Tower is a Contemporary skyscraper designed between 2010 and 2014 by Adrian Smith + Gordon Gill Architecture, in association with AAI Architects, and built between 2014 and 2020, for a reported $3.00 billion dollars, in New York, NY.
Its precise street address is 225 West 57th Street, New York, NY. You can also find it on the map here.
The Central Park Tower has received multiple architecture awards for its architectural design since 2020. The following is a list of such prizes and awards:
- 2021 CTBUH Awards in 2021
- AIA Chicago, Architecture XL, Honor Award in 2022
As is common in many New York buildings, several floor numbers are skipped, with the top floor labeled as 136, even though the structure physically has 98 floors above street level.