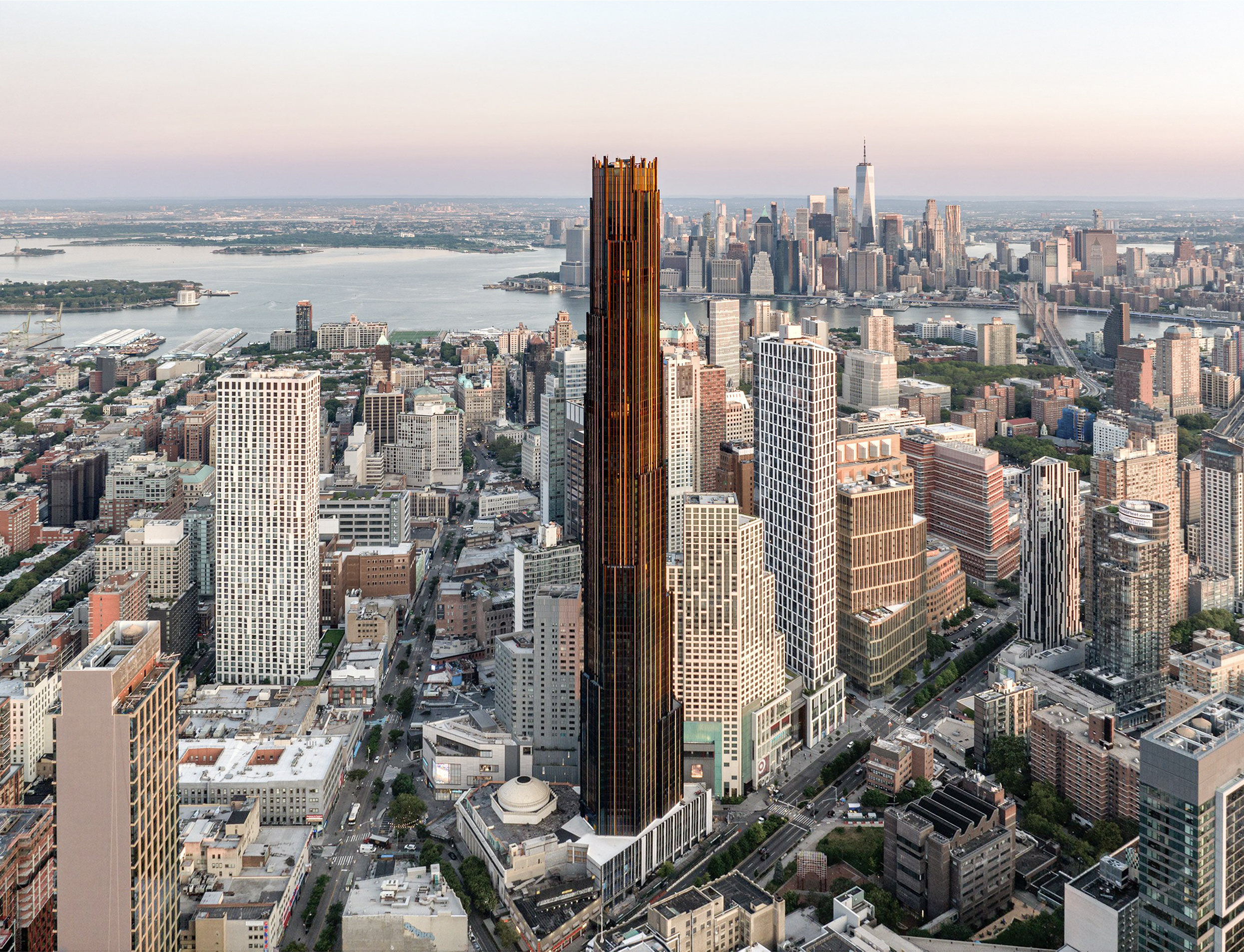
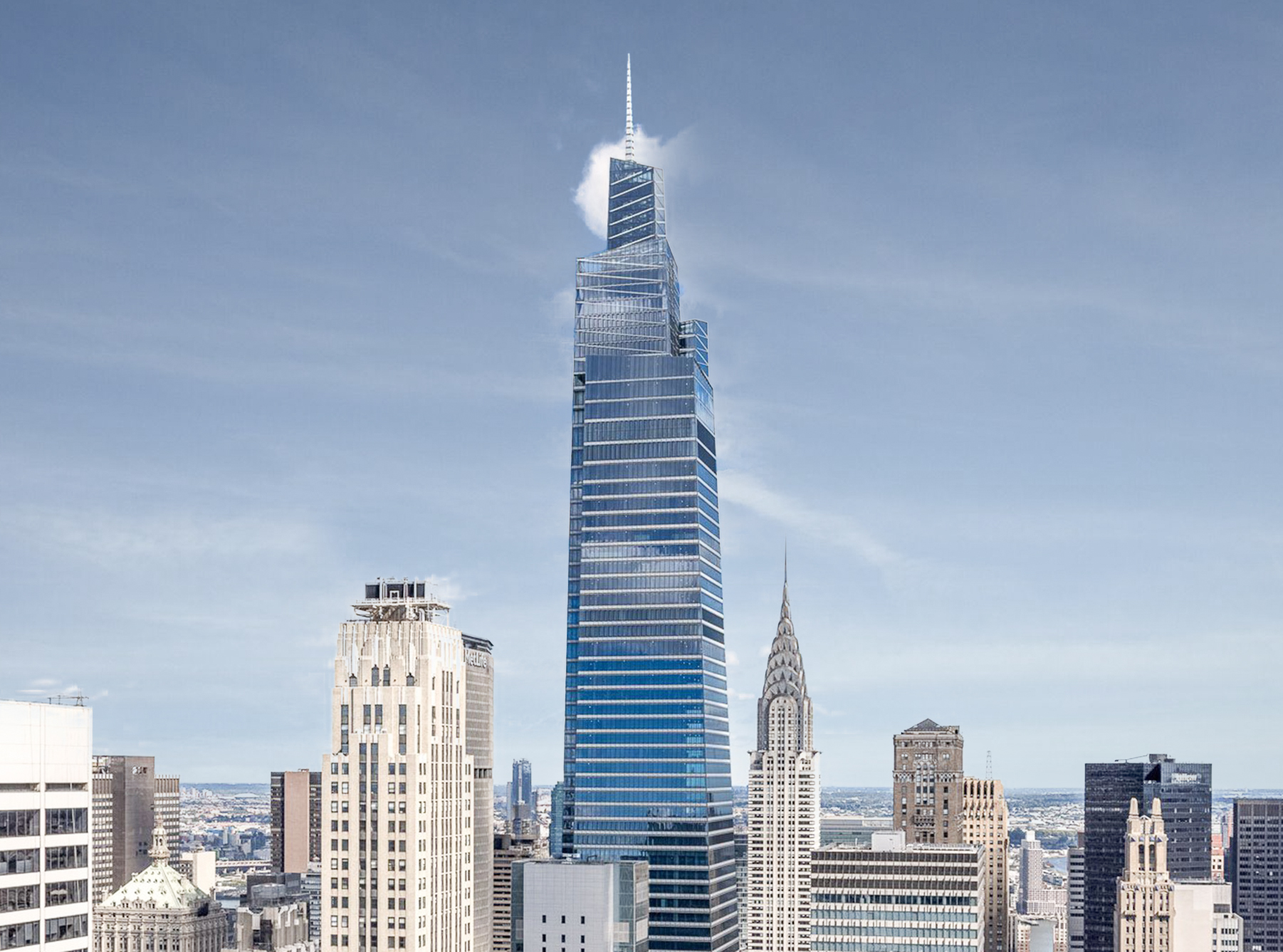
The Brooklyn Tower is a Contemporary skyscraper designed in 2015 by SHoP Architects, and built between 2017 and 2023 in New York, NY.
Brooklyn Tower is not the only name you might know this building by though. It is common for companies to want to attach their names to iconic buildings when they move in, or for the general public to come up with nicknames, and this one is no exception. The Brooklyn Tower is also known, or has been known as, Flatbush Tower, or 9 Dekalb Avenue.
Its precise street address is 9 DeKalb Ave, New York, NY. You can also find it on the map here.
The Brooklyn Tower incorporates at its base the historic Dime Savings Bank building, designed by Mowbray and Uffinger and built between 1906 and 1908, later expanded by Halsey, McCormack, and Helmer, and designated as a New York City Landmark in 1994.
At the time of its completion in 2023 the Brooklyn Tower incorporated solutions that were quite advanced at the time, these included the use of "augmented reality" (AR) technologies during its construction to allow the visualization of the tower for sales purposes.
Odor and airflow control systems were also installed in the trash chutes to mitigate unpleasant odors.