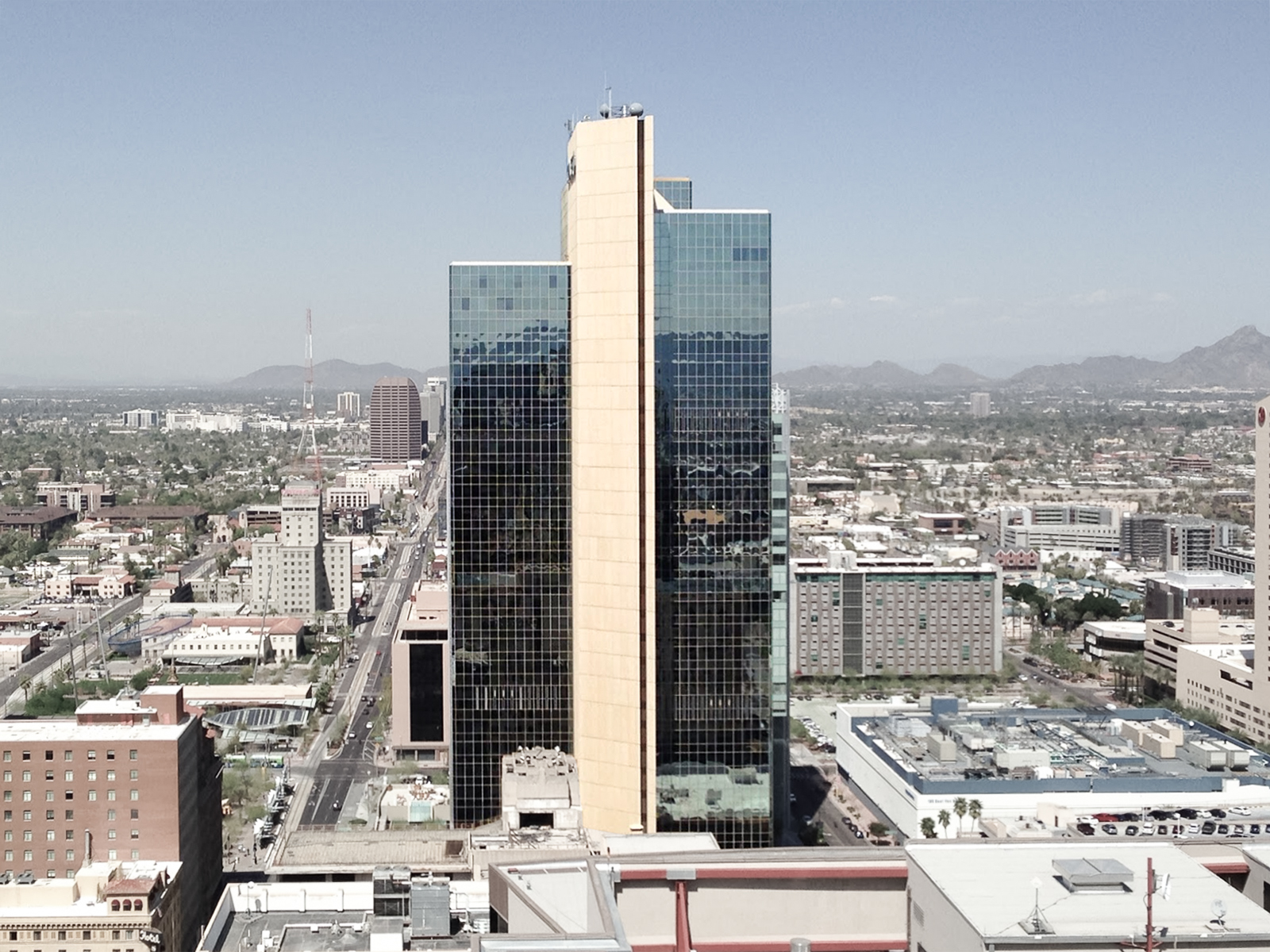
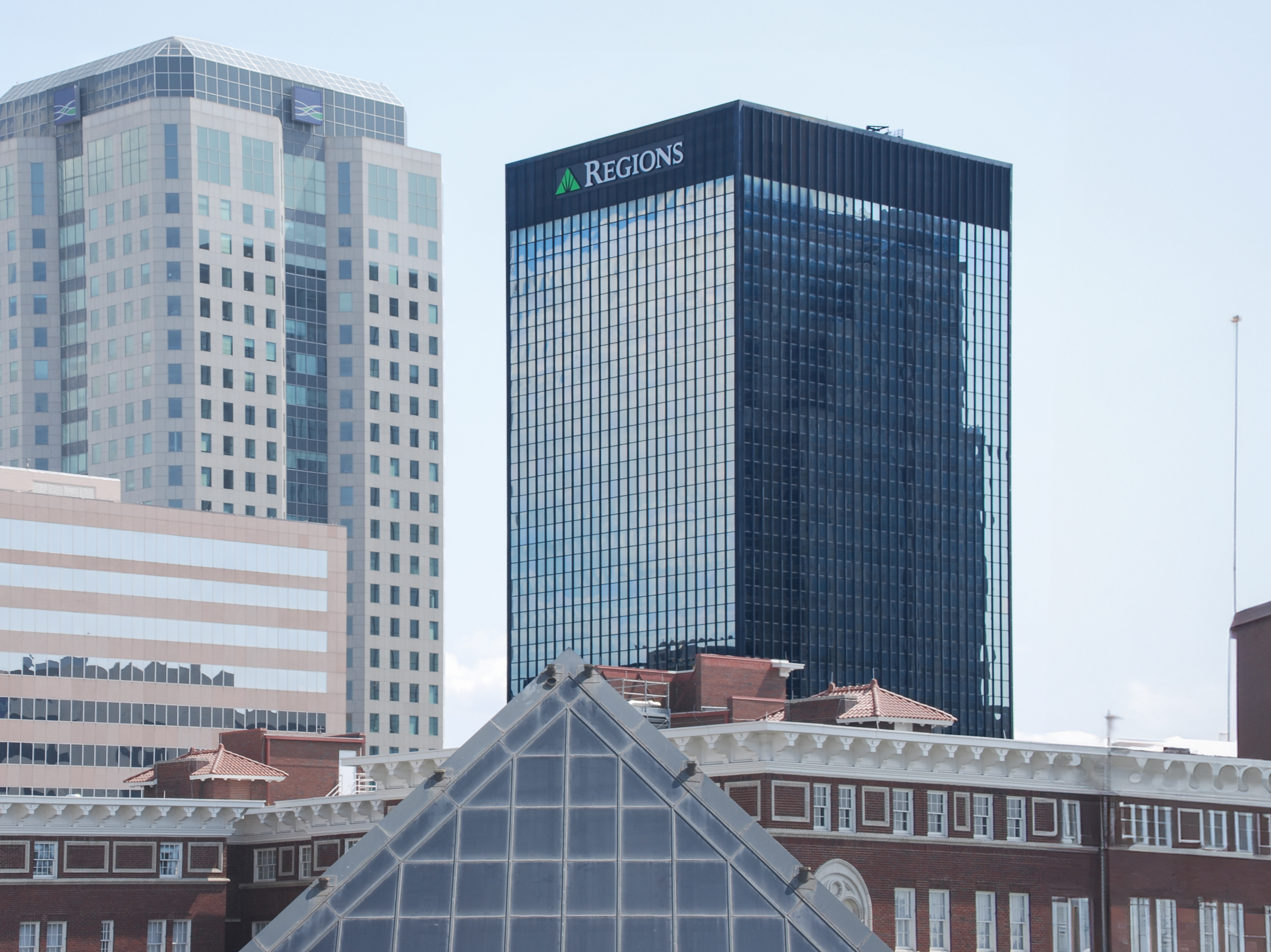
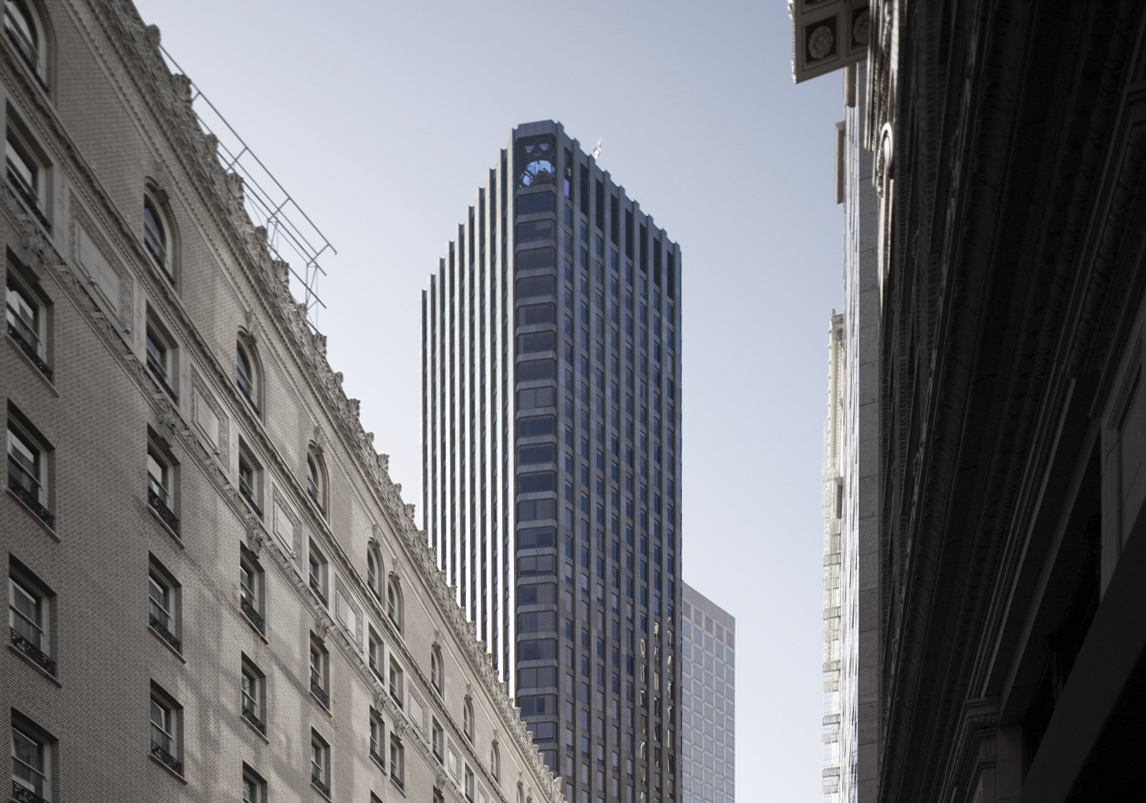
The Chase Tower is a Modern Style skyscraper designed by Welton Becket & Associates, in association with Guirey, Srnka, Arnold, & Sprinkle, and built between 1970 and 1972 in Phoenix, AZ.
Chase Tower is not the only name you might know this building by though. It is common for companies to want to attach their names to iconic buildings when they move in, or for the general public to come up with nicknames, and this one is no exception. The building has changed names several times over the years, and is also known as:
- Valley National Bank Building between 1972 and 1992.
- Valley Bank Center between 1993 and 2005.
- Chase Tower from 2005 until this day.
Its precise street address is 201 North Central Avenue, Phoenix, AZ. You can also find it on the map here.
The tower originally included a public observation area on the 39th floor, but it was closed during several redevelopments. Today the highest accesibe floor is the 38th.